In the fast-paced world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, innovation is the key to survival. Among the many groundbreaking concepts that have emerged, Proof of Importance (PoI) stands tall, reshaping the landscape of consensus mechanisms. In this article, we delve deep into the intricate realm of PoI, exploring its significance, its relationship with blockchain, and why this revolutionary concept is worth your attention.
What is Proof of Importance Mechanism?
The Proof-of-Importance consensus algorithm is designed to select block harvesters for a cryptocurrency network based on their level of importance within the network. The Proof-of-Importance mechanism, initially introduced by NEM, serves the purpose of determining the eligibility of network participants to contribute a block to the blockchain. This process is commonly referred to as harvesting. Nodes have the opportunity to receive transaction fees as compensation for successfully harvesting a block.
The dominance of Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) in the field is challenged by the emergence of Proof of Importance (PoI), which offers a novel viewpoint. In contrast to the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which assigns priority to miners based on their computational capabilities, or the Proof of Stake (PoS) approach, which places importance on the possession of a specific quantity of cryptocurrency, the Proof of Importance (PoI) consensus mechanism adopts a more comprehensive perspective. The system places emphasis on network participants who engage in frequent cryptocurrency transactions, it’s designed reward users who actively transact in a cryptocurrency by prioritizing miners based on the amounts and sizes of transactions made from their wallets
How Is Proof-of-Importance Calculated?
Unlike traditional systems, where mining tasks are assigned based on computational prowess, PoI calculates importance by considering various factors. These include the number and size of transactions, the amount of cryptocurrency held, and the entity’s activity within the network. By prioritizing users who actively engage with the cryptocurrency, PoI establishes a democratic and engaging system, fundamentally different from its predecessors.
How does PoI work in blockchain consensus mechanism?
Proof-of-Importance is a blockchain consensus mechanism that rewards nodes based on their contributions to the network, such as the number of transactions they process and the amount of cryptocurrency they hold. PoI is more efficient and sustainable than other consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Work (PoW), as it does not require nodes to compete with each other to solve complex mathematical problems.
The following is a concise exposition of the functioning principles of the Point of Interest (PoI) system:
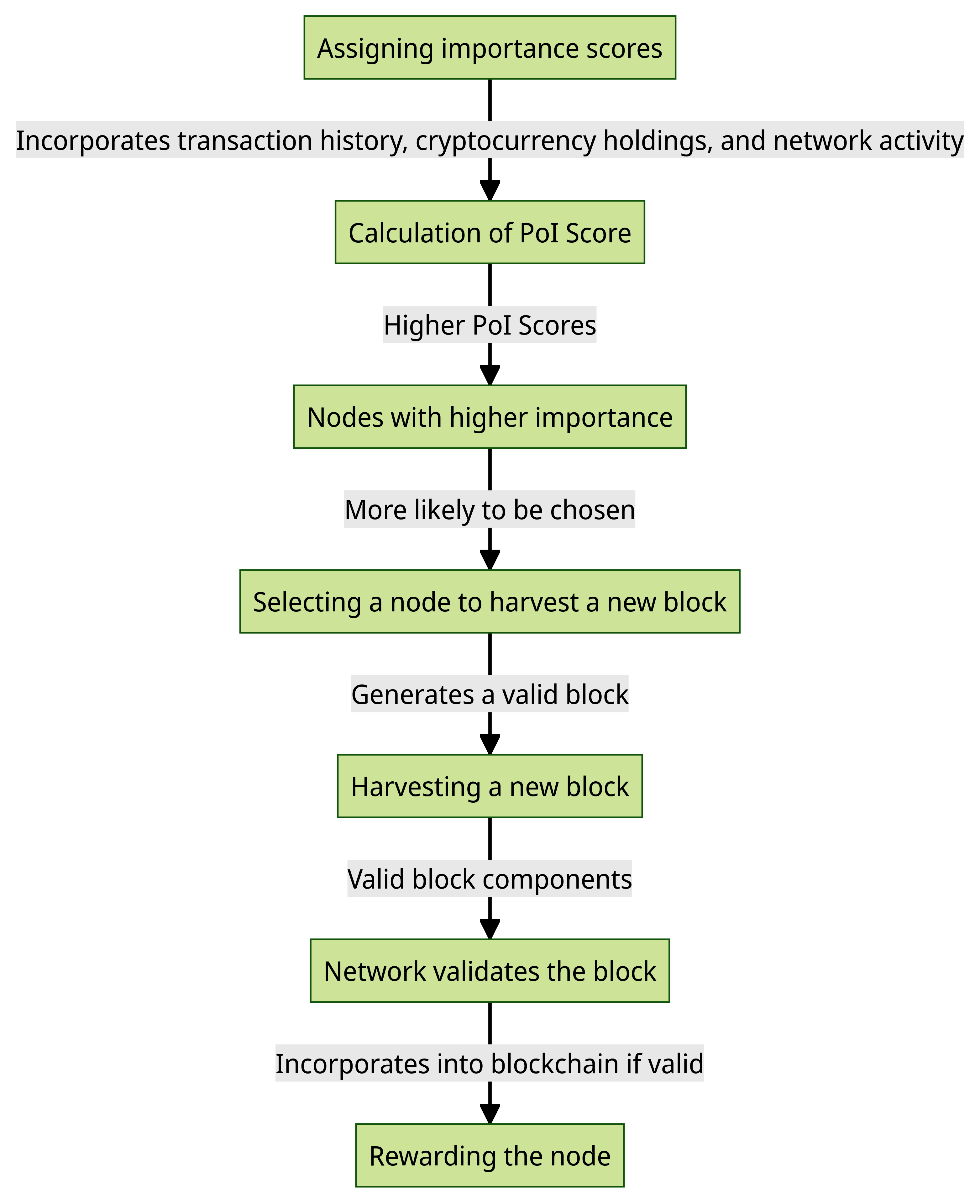
- An importance score is assigned to each node. The score is computed by taking into account various factors, including the transaction history of the node, the quantity of cryptocurrency it possesses, and its level of network engagement.
- Nodes that possess higher importance scores are more likely to be chosen for the purpose of harvesting a new block.
- In order to successfully acquire a new block, a node is required to generate a block that adheres to the established criteria and subsequently transmit it to the network.
- Upon the acceptance of a block by the network, a node is granted a modest quantity of cryptocurrency as a reward.
Below is a comprehensive elucidation of each individual step:
1. Assigning importance scores
The calculation of a node’s Proof of Importance score (PoI Score) incorporates several factors, including its transaction history, cryptocurrency holdings, and network activity. The selection and weighting of specific factors may vary depending on the particular algorithm employed for the Point of Importance (PoI) analysis.
In a general context, nodes that engage in a greater volume of transactions and possess larger quantities of cryptocurrency will exhibit elevated levels of importance. This phenomenon can be attributed to the fact that these nodes are exerting a more significant influence on the overall network.
2. Selecting a node to harvest a new block
Nodes that possess higher importance scores are more likely to be chosen for the purpose of harvesting a new block. This phenomenon occurs due to the network’s inclination to incentivize nodes that exhibit a higher level of contribution.
The selection process for nodes to harvest a new block is contingent upon the particular Proof-of-Importance algorithm employed. In a general context, nodes that possess higher importance scores are more likely to be chosen.
3. Harvesting a new block
In order to successfully acquire a new block, a node is required to generate a block that adheres to the established criteria and subsequently transmit it to the network. A valid block is defined as a block that encompasses all essential components, including the preceding block hash, the roster of transactions to be incorporated within the block, and the digital signature of the miner.
After successfully generating a valid block, a node proceeds to submit it to the network. Subsequently, the network undertakes the process of validating the block and subsequently incorporates it into the blockchain, contingent upon its adherence to the established criteria of validity.
4. Rewarding the node
Upon successfully mining a new block, a node is granted a modest quantity of cryptocurrency as a reward. The purpose of this reward is to provide an incentive for nodes to actively engage in the network and contribute to its security.
Advantages
The Proof-of-Importance consensus mechanism offers several advantages in comparison to alternative consensus mechanisms. This encompasses several advantages.
- Enhanced efficiency: In contrast to Proof-of-Work, Proof-of-Importance operates without necessitating nodes to engage in competitive solving of intricate mathematical problems. This characteristic renders PoI significantly more efficient.
- Enhanced scalability: The Proof-of-Importance consensus mechanism exhibits superior scalability compared to the Proof-of-Work mechanism, as it alleviates the need for nodes to expend substantial computational resources.
- The PoI consensus mechanism exhibits a diminished environmental footprint in comparison to PoW, owing to its lower energy consumption.
- Enhanced security: PoI exhibits a higher level of security compared to PoW, owing to its heightened resistance against potential network breaches by malicious actors.
Disadvantages
PoI also has a few drawbacks, including:
- Centralization: The Proof-of-Importance consensus mechanism has the potential to exhibit a higher degree of centralization compared to other consensus mechanisms. This is due to the fact that nodes with higher importance scores are more likely to be chosen for the task of harvesting a new block.
- Complexity: The implementation of Proof-of-Importance is characterized by a higher level of complexity compared to alternative consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Work (PoW)
In general, Proof-of-Importance (PoI) represents a promising consensus mechanism that exhibits the potential to enhance the efficiency, scalability, and sustainability of blockchain networks. The consensus mechanism in question is relatively recent, yet it has already found application in various practical blockchain initiatives.
Proof of Importance vs. Proof of Stake and Proof of Work
The Proof of Importance (PoI) is a consensus mechanism utilized in blockchain networks to incentivize nodes based on their contributions to the network. These contributions include the processing of transactions and the possession of cryptocurrency holdings. The Proof-of-Importance consensus mechanism exhibits greater efficiency and sustainability compared to alternative consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Work (PoW), due to its elimination of the need for nodes to engage in competitive solving of intricate mathematical problems.
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism employed in blockchain technology, wherein nodes are incentivized with rewards proportional to the quantity of cryptocurrency they commit as stake. Proof of Stake (PoS) is considered to be a more efficient and sustainable consensus mechanism compared to Proof-of-Work (PoW) due to its reduced demand for computational resources from participating nodes.
The Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism is a blockchain algorithm that incentivizes miners by allocating rewards proportionate to their computational resources utilized in the network. Proof-of-Work (PoW) is widely recognized as the oldest and most renowned consensus mechanism in the field. However, it is important to note that despite its prominence, PoW is considered to be the least efficient and sustainable among existing mechanisms.
Here is a comparison of the three consensus mechanisms:
| Consensus mechanism | Rewards | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proof-of-Importance (PoI) | Nodes based on their contributions to the network | More efficient and sustainable than PoW | Can be more centralized than other consensus mechanisms |
| Proof-of-Stake (PoS) | Nodes based on the amount of cryptocurrency they stake | More efficient and sustainable than PoW | Can be vulnerable to attacks from large holders of the cryptocurrency |
| Proof-of-Work (PoW) | Miners based on the amount of computing power they contribute to the network | The oldest and most well-known consensus mechanism | Less efficient and sustainable than PoI and PoS |
Which consensus mechanism is considered the most optimal?
The question at hand does not have a universally applicable solution. The optimal consensus mechanism for a given blockchain will be contingent upon its unique requirements.
For instance, blockchain networks that prioritize efficiency and sustainability may opt to employ Proof-of-Importance (PoI) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms. Blockchain networks that prioritize security often opt to employ the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism.
In order to determine the most suitable consensus mechanism for a given blockchain, it is essential to carefully evaluate the advantages and disadvantages associated with each mechanism, and subsequently select the one that aligns most effectively with the specific requirements of the blockchain in question.
The Intricacies of Proof-of-Importance Mechanism
The Role of Nodes in PoI
In PoI, nodes play a pivotal role. A node’s importance within the network is determined by its activity, the number of transactions it facilitates, and the corresponding cryptocurrency it holds. Unlike PoW, which demands raw computational power, PoI encourages a more nuanced involvement, where nodes are valued not just for their computing strength but for their active participation in the network’s transactions.
The Algorithm Behind PoI
Central to PoI’s success is its algorithm, which automatically assigns mining tasks to miners based on their transactional engagement. This unique algorithm ensures that the more an entity actively transacts, the higher its chances of harvesting a block. By prioritizing entities based on their transactional behavior, PoI fosters an ecosystem where active participation is not just valued but rewarded.
PoI: A Step Towards Decentralization and Equality
Overcoming the Constraints of Centralization
One of the foremost advantages of Proof-of-Importance lies in its inherent resistance to centralization. In contrast to the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which relies on computing power as the primary determinant, the Proof-of-Importance (PoI) consensus mechanism employs an automated priority system to ensure that the entity possessing the greatest capacity for computing power is duly incentivized. The democratic approach serves as a safeguard against the concentration of power, guaranteeing that no singular entity can establish a monopoly over the network.
Enhancing the Agency of Small-scale Actors
In the context of the television series Proof-of-Importance, it is observed that even entities with constrained resources have the ability to flourish. The prioritization of entities within the system is determined by their level of engagement with the cryptocurrency, rather than solely relying on their computational power. This implies that individuals with limited resources but high levels of enthusiasm and active engagement have the opportunity to achieve benefits, thereby promoting a more inclusive and egalitarian environment.
The Future of Blockchain: PoI’s Potential and Challenges
PoI and Environmental Sustainability
As the world becomes increasingly environmentally conscious, PoI’s energy-efficient approach becomes a beacon of hope. Unlike PoW, which demands massive amounts of electricity, PoI’s emphasis on transactional engagement reduces the energy footprint significantly. This shift towards a greener consensus mechanism aligns with the global push for sustainable technologies, making PoI a potential game-changer in the crypto sphere.
Challenges and Pitfalls
While PoI brings forth a myriad of advantages, it is not without its challenges. Ensuring a fair and accurate calculation of importance, preventing gaming of the system, and addressing potential vulnerabilities are areas that demand continuous attention. However, with the collective intelligence of the crypto community, these challenges can be overcome, paving the way for a robust PoI ecosystem.
Real-world use cases of PoI
The Proof-of-Importance blockchain consensus mechanism has gained prominence in recent years and has been implemented in various practical applications. Several prominent instances can be cited as examples, such as:
- NEM: The NEM platform is a public blockchain that employs the Proof-of-Importance (PoI) consensus mechanism to ensure the security of its network. NEM serves multiple functions, encompassing payment processing, supply chain administration, and asset supervision.
- Symbol: Symbol is a publicly accessible blockchain platform that underwent a fork from NEM in the year 2021. Symbol also employs Proof-of-Importance as a means of ensuring the security of its network. Symbol is primarily concerned with offering a platform that is both scalable and secure for enterprise applications.
- Nano: Nano is a digital currency that employs a Proof-of-Importance (PoI) consensus mechanism to safeguard its network. Nano is renowned for its ability to facilitate rapid and cost-free transactions.
- Sleek: Sleek is a digital currency that employs the Proof-of-Importance consensus mechanism to ensure the security and integrity of its network. Sleek prioritizes the provision of a platform that ensures privacy and security in payment transactions.
- Ardor: Ardor is a publicly accessible blockchain platform that employs Proof-of-Importance as a mechanism to safeguard its network. The primary objective of Ardor is to serve as a comprehensive framework for the construction and implementation of child chains.
- Catapult: The Catapult blockchain platform employs Proof-of-Importance as a mechanism to ensure the security of its network. Catapult is a derivative of Ardor that has been specifically engineered to enhance its scalability and security features.
In addition to the aforementioned specific projects, the utilization of PoI extends to various other applications, including:
- Enterprise blockchain platforms: Several enterprise blockchain platforms are currently employing the Proof-of-Importance consensus mechanism as a means to enhance the security of their networks. This is due to the fact that Proof-of-Importance exhibits greater efficiency and scalability compared to alternative consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Work (PoW).
- Supply chain management: Several companies are employing PoI (Proof of Importance) as a means to monitor and effectively oversee their supply chains. The reason for this is that Proof-of-Importance has the capability to offer a secure and tamper-resistant method for monitoring the transportation of commodities.
- Asset management: Many companies are utilizing the concept of Proof-of-Importance as a means to effectively manage their assets. The reason for this is that Proof-of-Importance can offer a secure and efficient mechanism for monitoring the ownership and transfer of assets.
In general, Proof-of-Importance exhibits promising attributes as a consensus mechanism, holding the capacity to fundamentally transform the manner in which blockchain networks are safeguarded. The consensus mechanism under consideration is relatively nascent; nevertheless, it has already found application in several tangible projects.
NEM and the Catapult blockchain platform
The NEM platform is a publicly accessible blockchain system that employs the Proof-of-Importance consensus mechanism to ensure the security and integrity of its network. NEM serves multiple functions, encompassing payment processing, supply chain administration, and asset supervision.

In the year 2021, NEM introduced a novel blockchain platform named Catapult. Catapult is a derivative of the NEM blockchain platform, specifically engineered to enhance scalability and bolster security measures. The Catapult platform employs the PoI consensus mechanism, similar to that of NEM, while also incorporating additional functionalities such as an enhanced transaction format and an innovative smart contract engine.
Several companies are utilizing catapult technology to facilitate the development and implementation of blockchain applications. An instance of this can be observed in the utilization of Catapult by the company Food Trust, wherein they are engaged in the development of a platform that employs blockchain technology for the purpose of monitoring and overseeing food supply chains.
PoI is a promising consensus mechanism that has the potential to revolutionize the way that blockchain networks are secured. The consensus mechanism under consideration is relatively nascent, yet it has already found application in various practical endeavors, including NEM and Catapult.
Conclusion: Embracing the PoI Revolution
Within the broader context of blockchain technology, the concept of Proof of Importance arises as a dynamic element, interconnecting various aspects to form a cohesive narrative centered around inclusiveness, equity, and advancement. The departure from traditional consensus mechanisms represents a significant shift in paradigm, placing greater emphasis on active participation rather than computational ability.
As society progresses, acknowledging the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) revolution becomes imperative, given its profound capacity for transformation and the accompanying obstacles it entails. Through a comprehensive comprehension and effective resolution of these intricacies, the cryptographic community can effectively utilize the genuine potential of Proof of Importance (PoI), thereby establishing a future for blockchain technology that is characterized by enhanced democracy, sustainability, and engagement.
Key Takeaways:
- PoI prioritizes network participants based on their transactional engagement and cryptocurrency holdings.
- PoI’s algorithm assigns mining tasks automatically, promoting an inclusive ecosystem.
- PoI stands against centralization, ensuring a more democratic and equal network.
- Its energy-efficient approach aligns with global efforts for environmental sustainability.
- Challenges include fair importance calculation and guarding against system exploitation.
FAQs
What is Proof-of-Importance (PoI) in the context of blockchain technology?
PoI is a consensus algorithm selecting block harvesters based on participants’ network importance. It assesses transaction activity and cryptocurrency holdings for block eligibility.
How does Proof-of-Importance (PoI) differ from Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS)?
Unlike PoW’s computational emphasis and PoS’s focus on holdings, PoI values active transactions, fostering a democratic and engaging ecosystem.
What factors does PoI consider in calculating importance for network participants?
PoI factors in the number and size of transactions, cryptocurrency holdings, and participant activity, prioritizing those engaged in cryptocurrency transactions.
What role do nodes play in the PoI consensus mechanism?
Nodes’ importance in PoI is determined by their transactional activity and cryptocurrency holdings. Unlike PoW, PoI values nodes for both their computing strength and transaction participation.
How does PoI contribute to environmental sustainability in blockchain technology?
PoI reduces the energy footprint significantly compared to PoW by emphasizing transactional engagement, aligning with global efforts for sustainable technologies.







