In the realm of storage solutions, conventional storage can be aptly compared to a well-established corporation that functions as a centralized entity, overseeing a communal warehousing facility where individuals can securely store their personal belongings. Decentralized storage is a revolutionary concept that involves a distributed system where individuals maintain ownership of their personal belongings within their own homes while also collectively ensuring their security through mutual assistance.
The implementation of blockchain technology for storage purposes can be compared to the existence of individual lockboxes that are highly secure for each item, guaranteeing protection against errors and hazards. In addition, it is worth noting that any challenges faced by an individual do not have a negative effect on others.

Introduction
Experience the awe-inspiring metamorphosis of data storage and sharing as it unfolds in real time. Witness the breathtaking metamorphosis that has utterly reshaped the landscape, propelling it into a thrilling new epoch brimming with boundless possibilities.
Embark on an immersive exploration of the remarkable odyssey of internet technology, a revolutionary force that has irrevocably reshaped the fabric of our existence. Witness the remarkable ascent of cloud storage, a revolutionary and seamlessly integrated business model that has swiftly become a fundamental component of our daily existence.
Discover the extraordinary convenience and unparalleled flexibility that lie in store for you, courtesy of our groundbreaking technology. Introducing our cutting-edge solutions that revolutionize data storage and sharing, bidding farewell to the burdensome process.
“Data is the new oil.”
British mathematician – Clive Humby (2006)
In 2006, the renowned Clive Humby made a profound declaration that continues to reverberate across diverse sectors: “Data is the new oil.“

In our modern society, the undeniable significance of data has become increasingly apparent. In parallel to the way oil fuels our machines and propels societal progress, data has emerged as the pivotal catalyst for innovation and the attainment of success.
The immense potential and transformative capabilities of this phenomenon should not be underestimated. Its ability to unlock extraordinary opportunities and mold the course of our future is truly remarkable.
In our modern era, where knowledge reigns supreme, individuals who harness the potential of data are poised for great success. In an era where our online activities and digital presence have become inseparable from our daily lives, the profound importance of this statement emerges, revealing its timeless significance.
As we delve into the depths of our interconnected world, the value of our information becomes increasingly intertwined with the fabric of our existence.
Traditional centralized storage solutions, despite their apparent accessibility and convenience, have been found to possess certain drawbacks that warrant closer examination.
Unveiling the Incredible Truth: Users Frequently Disclose Their Precious Data, Prompting Concerns over Privacy, Security, and Vulnerability of Sensitive Information.
Discover the revolutionary advancements that have revolutionized the landscape of distributed storage systems. Bid adieu to the limitations enforced by centralized systems and the necessity of depending on third-party establishments for trust. Prepare to be captivated by the awe-inspiring possibilities that lie within the realm of blockchain technology, as we embark on a journey into a groundbreaking era of limitless creativity and ingenuity.
Arweave: The Revolutionary Answer to Data Permanence and Censorship Worries
In an era where data security and freedom of expression are paramount concerns, Arweave emerges as a groundbreaking solution. With its cutting-edge technology, Arweave offers users an unparalleled sense of peace of mind when it comes to data permanence and protection against censorship.
Arweave’s innovative approach to data storage ensures that your valuable information remains intact and accessible for the long term. By utilizing a unique blockchain-based system, Arweave guarantees the immutability and permanence of your data, eliminating the risk of loss or tampering.
Moreover, Arweave’s Arweave offers users an unparalleled level of security and resilience, eliminating worries and providing peace of mind.
Filecoin: Transforming the Landscape of Decentralized Storage
Filecoin, the groundbreaking platform poised to transform the landscape of decentralized storage, has arrived on the scene. This innovative technology promises to revolutionize the way we perceive and utilize storage systems. Filecoin, the groundbreaking storage network, is making waves in the tech world by leveraging the immense potential of the state-of-the-art InterPlanetary File System (IPFS). Filecoin offers users an unprecedented storage experience that is both dynamic and fully distributed. Introducing a groundbreaking technological advancement that holds the key to a multitude of limitless possibilities!
In an exciting development, customers and storage miners now have the opportunity to engage in a vibrant marketplace for storage and retrieval services. Prepare yourself for an exhilarating journey into a realm brimming with boundless potential! Get ready to embark on an extraordinary storage journey like never before with Filecoin.
Siacoin: Revolutionizing Data Storage with Smart Contract Technology
In the ever-evolving world of data storage, a groundbreaking solution has emerged – Siacoin. This innovative technology harnesses the power of smart contracts to provide a secure and reliable means of storing data effortlessly. With the exponential growth of digital information, the need for robust and trustworthy data storage has become paramount. Traditional methods often fall short in terms of security and reliability, leaving individuals and businesses vulnerable to data breaches and loss.
Siacoin aims to address these concerns by leveraging the potential of smart contract technology. Smart contracts, built on blockchain technology, are self-executing agreements with predefined rules. Siacoin utilizes these contracts to create a decentralized network of storage providers, ensuring data is distributed across multiple locations.
How does Decentralized Storage work?
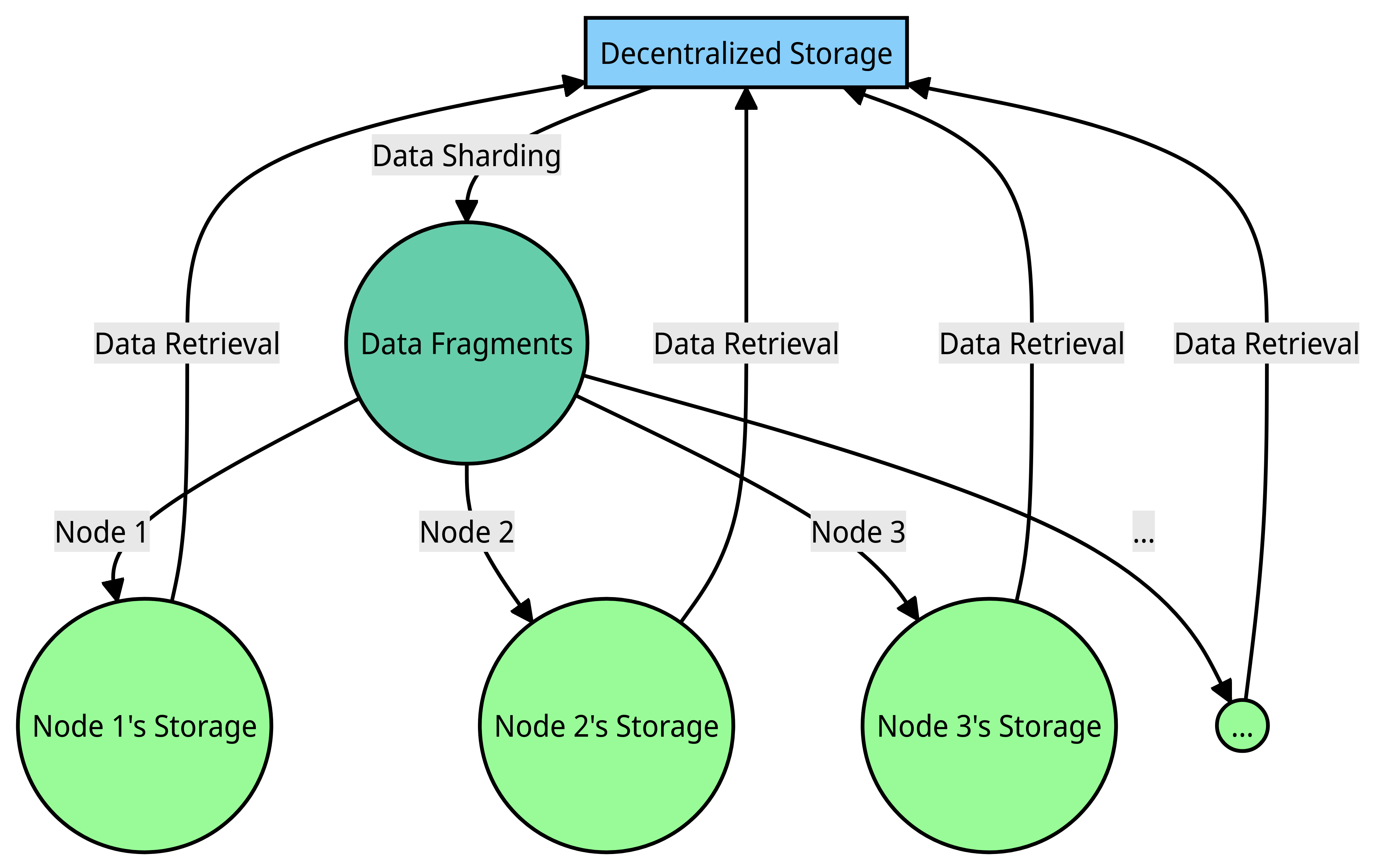
Decentralized storage, a cutting-edge technique, utilizes peer-to-peer (P2P) networks to distribute and store data across numerous nodes or devices. Through a fascinating technique called sharding, data is meticulously divided into smaller fragments, resembling puzzle pieces. These fragments are then distributed across a network of computers, known as nodes, owned by individuals. This ingenious approach ensures secure and easily accessible data, even in the face of potential disruptions or failures.
In the captivating world of decentralized networks, each node plays a crucial role by offering its share of storage space and bandwidth. Like interconnected puzzle pieces, these nodes work harmoniously to store and retrieve data from one another, showcasing remarkable collaboration and efficiency within the network.
A defining feature of this groundbreaking system is the absence of a central authority or intermediary overseeing data and network management. In the realm of data storage, decentralized storage harnesses the power of blockchain or other distributed ledger technologies (DLTs). This innovative method not only effectively manages the storage network but also provides incentives for nodes to contribute their valuable storage resources.
Decentralized Storage vs Centralized Storage
Blockchain-based decentralized data storage systems are revolutionizing the way we manage data, marking a significant shift in the field of data management. These innovative systems offer a multitude of advantages that surpass the capabilities of traditional centralized storage solutions.
The advantages of blockchain technology can be attributed to its fundamental principles and unique features. One key aspect is its decentralized nature, which ensures that no single entity has control over the entire system. This decentralization promotes transparency, security, and trust among participants.
Additionally, blockchain’s innovative data storage capabilities allow for the secure and immutable recording of transactions and information. These features make blockchain a promising technology with numerous potential applications across various industries. Decentralized data storage systems, like any groundbreaking technology, present a unique set of challenges that must be addressed in order to fully harness their capabilities.

The Advantages of Decentralized Storage Over Centralized Storage
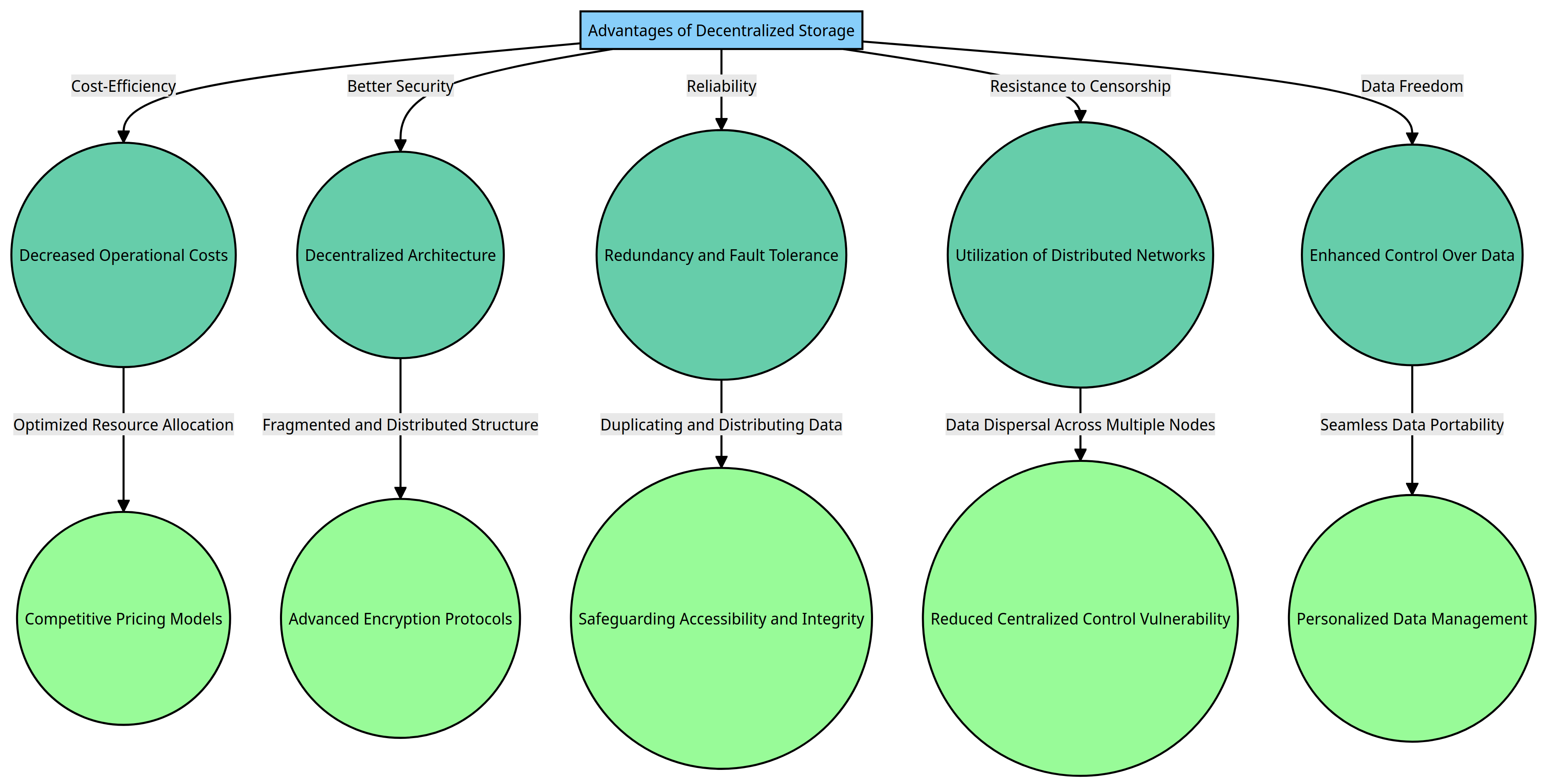
Cost-Efficiency
Decentralized Data Storage Systems have gained significant attention due to their remarkable cost-efficiency. By harnessing the power of distributed networks and minimizing dependence on centralized infrastructure, these innovative systems have the potential to significantly decrease operational costs and alleviate the burden of resource-intensive maintenance. The implementation of optimized resource allocation and competitive pricing models has the potential to greatly enhance the cost-effectiveness of data storage.
Better Security
The elevated level of data security in these storage systems is a direct result of their decentralized architecture. In a groundbreaking development, data has been revolutionized with a fragmented and distributed structure across multiple nodes. This innovative approach brings about a significant reduction in the vulnerability to both single points of failure and data breaches. The process of fragmentation, when combined with advanced encryption protocols, plays a crucial role in enhancing data privacy and safeguarding against unauthorized access.
Reliability
Decentralized storage solutions are revolutionizing the way we think about reliability, thanks to their innovative approach of embracing redundancy and fault tolerance. In the realm of data management, the process of duplicating and distributing data across various nodes plays a crucial role in safeguarding its accessibility and integrity.
This strategic approach serves as a robust defense mechanism, allowing data to persist even in the presence of hardware failures or disruptions in the network.
By replicating data across multiple locations, the risk of losing valuable information is significantly reduced, ensuring that users can rely on the availability and reliability of their data. The ability to withstand and recover from disruptions is of greatest significance for businesses that heavily rely on continuous and uninterrupted access to data.
Resistance to Censorship
Decentralized Data Storage Systems possess a remarkable characteristic that sets them apart: their ability to withstand censorship and external control. In order to address the potential risks of data manipulation or censorship by a single authority, a promising solution has emerged: the utilization of distributed networks.
These systems disperse data across multiple nodes, reducing the vulnerability of centralized control. The attribute being discussed here holds significant value in situations where the protection of data integrity and accessibility from external influences is of the highest priority.
Data Freedom
Decentralized storage has emerged as a groundbreaking solution, granting users a previously unavailable degree of control over their data and liberating them from traditional constraints. Decentralized systems offer a revolutionary approach to data management, setting them apart from traditional centralized models. Unlike their counterparts, which often impose proprietary constraints on data, decentralized systems prioritize the seamless movement and access of information without any form of lock-in or restrictions.
In a groundbreaking development, users are now empowered with enhanced control over their valuable data. This newfound control not only facilitates seamless data portability but also opens up a world of possibilities for more adaptable and personalized data management strategies.
Decentralized Data Storage Systems have emerged as a groundbreaking solution that revolutionizes the way we manage data. By incorporating key qualities such as enhanced security, heightened reliability, and optimized cost efficiency, these systems are reshaping the landscape of information technology.
What Are the Limitations of Decentralized Storage?
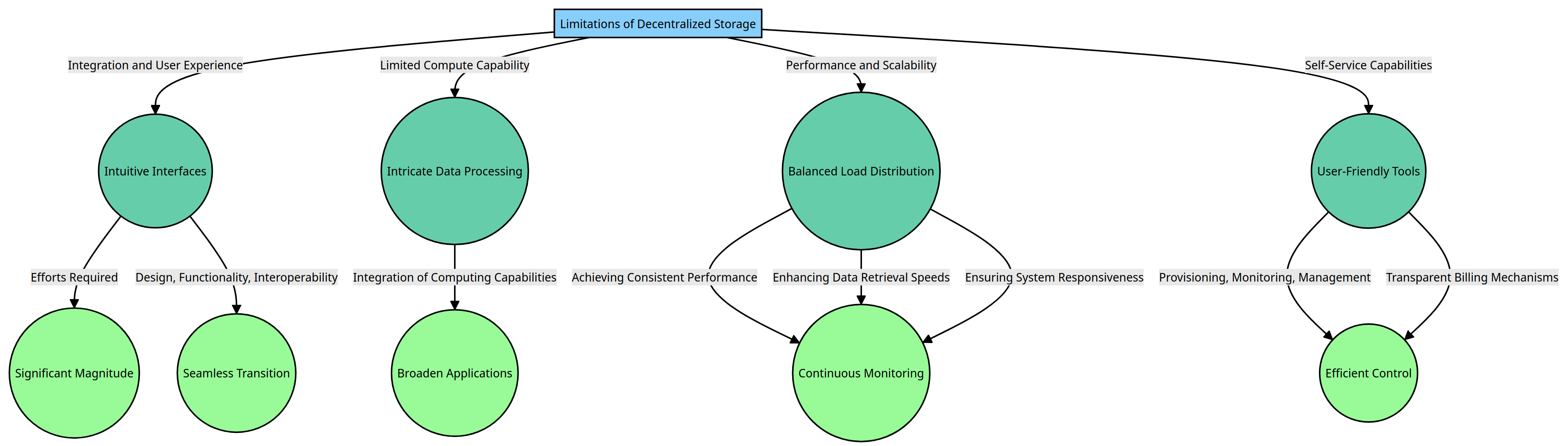
Decentralized data storage systems encounter several challenges.
Integration and User Experience
The seamless integration of decentralized data storage systems with existing applications and workflows can present a significant challenge. Efforts of significant magnitude may be necessary for the development of intuitive and user-friendly interfaces that effectively facilitate data migration, retrieval, and management across various systems, as suggested by recent research. Design, functionality, and interoperability are crucial factors when it comes to providing a seamless user experience during the shift from traditional to decentralized storage paradigms.
Limited Compute Capability
Decentralized data storage, although highly efficient in distributing and retrieving data, often falls short in terms of computational power compared to its traditional centralized counterparts. The constraint mentioned above poses a potential obstacle to carrying out intricate data processing tasks within the decentralized storage environment. The integration of powerful computing capabilities into decentralized storage networks presents a fascinating technical hurdle that demands ingenious solutions in order to broaden the scope of potential applications.
Performance and Scalability
The performance and scalability of storage systems can be influenced by their decentralized nature. Distributing data across multiple nodes presents a complex challenge in maintaining consistent and predictable performance levels. In the realm of network management, achieving balance in load distribution, enhancing data retrieval speeds, and ensuring system responsiveness as demand increases are perpetual endeavors that necessitate continuous monitoring, optimization, and infrastructure improvements.
Self-Service Capabilities
In a recent study, we have found that decentralized storage systems may fall behind their centralized counterparts when it comes to providing extensive self-service capabilities. This finding, highlighted in a scientific paper, sheds light on the potential limitations of decentralized storage systems in meeting the growing demand for user-friendly and convenient features. The task of incorporating user-friendly tools for the provisioning, monitoring, and management of storage resources in decentralized networks poses a significant challenge. Meticulous design and development are crucial in enabling users to have efficient control over their data, improving storage configurations, and ensuring transparent billing mechanisms.
In order to tackle these formidable challenges, a comprehensive approach is required, encompassing cutting-edge technological advancements, cautious strategic foresight, and a strong emphasis on designing solutions that prioritize the needs and experiences of users. In the ever-changing world of decentralized data storage, it is crucial to have solutions that improve integration, performance, and user accessibility. These advancements are key to unlocking the vast possibilities of this transformative paradigm.
Comparison table
In the ever-changing world of data storage, there are two main players: the Decentralized Data Storage System and the Centralized Storage System. These two paradigms are vying for the top spot in the industry. Discover a world of diverse philosophies and architectural approaches within these systems. Each one comes with its own special advantages and challenges. In this brief comparison from Table 1, we will explore the key differences between these two approaches. By doing so, we hope to provide a clearer understanding of how they impact data security, control, scalability, and other important factors.
| Centralized Data Storage | Decentralized Data Storage | |
| Strength | Efficient Operations Seamless Integration Enhanced Gateway User Self-services Options | Cost-effectiveness Robust Security Consistent Reliability Censorship-resilience Flexible Data Mobility |
| Weakness | Potential Vendor Dependency Uncertain Expenses Single Point of Failure Privacy and Censorship Concerns | Integration and User Experience Challenges Limited Data Processing Capability Performance Assurance Maturing Self-service Capabilities |
In the realm of data storage, a compelling comparison can be made between Centralized Data Storage and Decentralized Data Storage. Each approach presents distinct advantages and disadvantages, making this a topic of significant interest and importance.
Centralized Data Storage involves consolidating data in a single location or server. This approach offers notable advantages. Firstly, it enables efficient management and control of data, as all information is stored in one central repository. This centralized nature simplifies data access, streamlines operations, and makes data manipulation easier for organizations. Additionally, centralized storage often provides enhanced security measures. By consolidating data, organizations can implement robust security protocols, ensuring data safety.
Centralized storage, exemplified by industry leaders like Amazon AWS, demonstrates remarkable operational efficiency through user interface enhancements and supplementary offerings. This cutting-edge system seamlessly integrates with various applications, including analytics, data lakes, ERPs, CRMs, and DevOps tools. What sets it apart is its ability to deliver consistent and reliable performance due to meticulous infrastructure management. The centralized model not only facilitates self-service options but also proves to be cost-effective compared to traditional cloud providers.
Centralized Data Storage, despite its numerous strengths, also exhibits certain weaknesses. The issue of vendor lock-in presents a significant hurdle, potentially leading to the arduous task of data migration. The volatile nature of expenses, particularly in relation to bandwidth and API usage, can result in unforeseen financial burdens.
The susceptibility of the centralized architecture to hacks, attacks, or outages is a cause for concern when it comes to ensuring data security. In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, concerns surrounding censorship and privacy breaches have become increasingly prominent.
One pressing issue is the potential for governments to demand access to data from centralized providers, posing a significant risk to individuals and their personal information.
Decentralized Data Storage, on the other hand, offers a compelling solution that effectively tackles several of these concerns. The enhanced security and reliability of a network is achieved through the distribution of data across a network of nodes, effectively eliminating the presence of single points of failure. In a remarkable feat of technological innovation, this system has been designed to safeguard data privacy and integrity, exhibiting an impressive resistance to censorship and remaining impervious to governmental pressures.
In addition, this technology provides users with the freedom to access and transfer their data seamlessly between different service providers, eliminating any restrictions or additional expenses. Furthermore, it has the potential to offer significant cost savings, especially when compared to the potentially inflated prices imposed by conventional providers.
However, the concept of Decentralized Data Storage is not without its own vulnerabilities. The current state of the technology is hindered by its inability to efficiently perform queries and computations on the stored data, which restricts its usefulness in specific scenarios. The challenge of performance variability arises from the diverse capacities and locations of storage hosts, also known as miners. This variation in performance makes it difficult to establish standardized guarantees for performance. The ongoing development of self-service capabilities is having a significant impact on the user-friendliness of various systems.
In a fascinating analysis, it has been discovered that there exists a delicate balance between centralized operational excellence and cost-effectiveness, and the decentralized model’s remarkable advantages in terms of security, data freedom, and potential cost savings. When it comes to deciding between these two options, the determining factors lie in the specific use cases, performance requirements, and the sensitivity of the data involved. As the paradigms of data storage continue to progress, the future of this field is being shaped by a constant stream of technological advancements. These advancements are poised to tackle the strengths and weaknesses of existing data storage solutions, paving the way for a more efficient and solid future.
Features and Technical Comparison
| Current Market Cap | Consensus Algorithm | Data Replication & Retrieval | Encryption | Smart Contract Execution | Minimum Hosting Requirements | |
| Filecoin | ~$1.52B | Proof of Spacetime (PoSt) & Proof of Replication (PoR) | Users determine number of replicated copies | Users choose encryption of stored data | Utilizes Filecoin Virtual Machine (FVM) | CPU: 8 cores RAM: 137GB Hard Drive: 1.1TB |
| Arweave | ~$546M | Succinct Proof of Random Access (SPoRA) | Data stored by miners, replicated over 16 times | Users choose encryption of stored data | ‘Lazy’ SmartWeave contracts executed and validated by users, not the network | CPU: 6 cores RAM: 8.6GB Hard Drive: 4TB |
| Storj | ~$81M | Proof of Availability (PoA) | Data split into 80 pieces, 29 needed for retrieval | Automatically encrypted with AES-256 algorithm | No smart contract capability | CPU: 1 cores RAM: 2GB Hard Drive: 550GB |
| Sia | ~$214M | Proof of Work (PoW) | Data split into 30 pieces, 10 needed for retrieval | Automatically encrypted with Threefish algorithm | File contracts enforce agreements | CPU: 4 cores RAM: 8G Hard Drive: 64GB |
| BitTorrent | ~$851M | Proof of Stake (PoS) | Data split into 30 pieces, 10 needed for retrieval | Users choose encryption of stored data | Utilized BitTorrent-Chain Virtual Machine (BTTCVM) | CPU: 1 cores RAM: 1GB Hard Drive: 32GB |
| Amazon S3 | ~$1.5T | N/A | Users select files to replicate within regions | Users can enable server-side encryption using AES-256 algorithm | N/A | N/A |
Real-life example of Decentralized Storage
Filecoin is a decentralized storage network that allows users to rent storage space from other computers around the world. Filecoin uses a blockchain to record storage and retrieval transactions, as well as to verify that data is stored securely.
Filecoin works on three main groups:
- Client: A user who wants to store their data.
- Storage miner: A computer that provides storage space for a client’s data.
- Retrieval miner: A computer that helps a client retrieve their data.
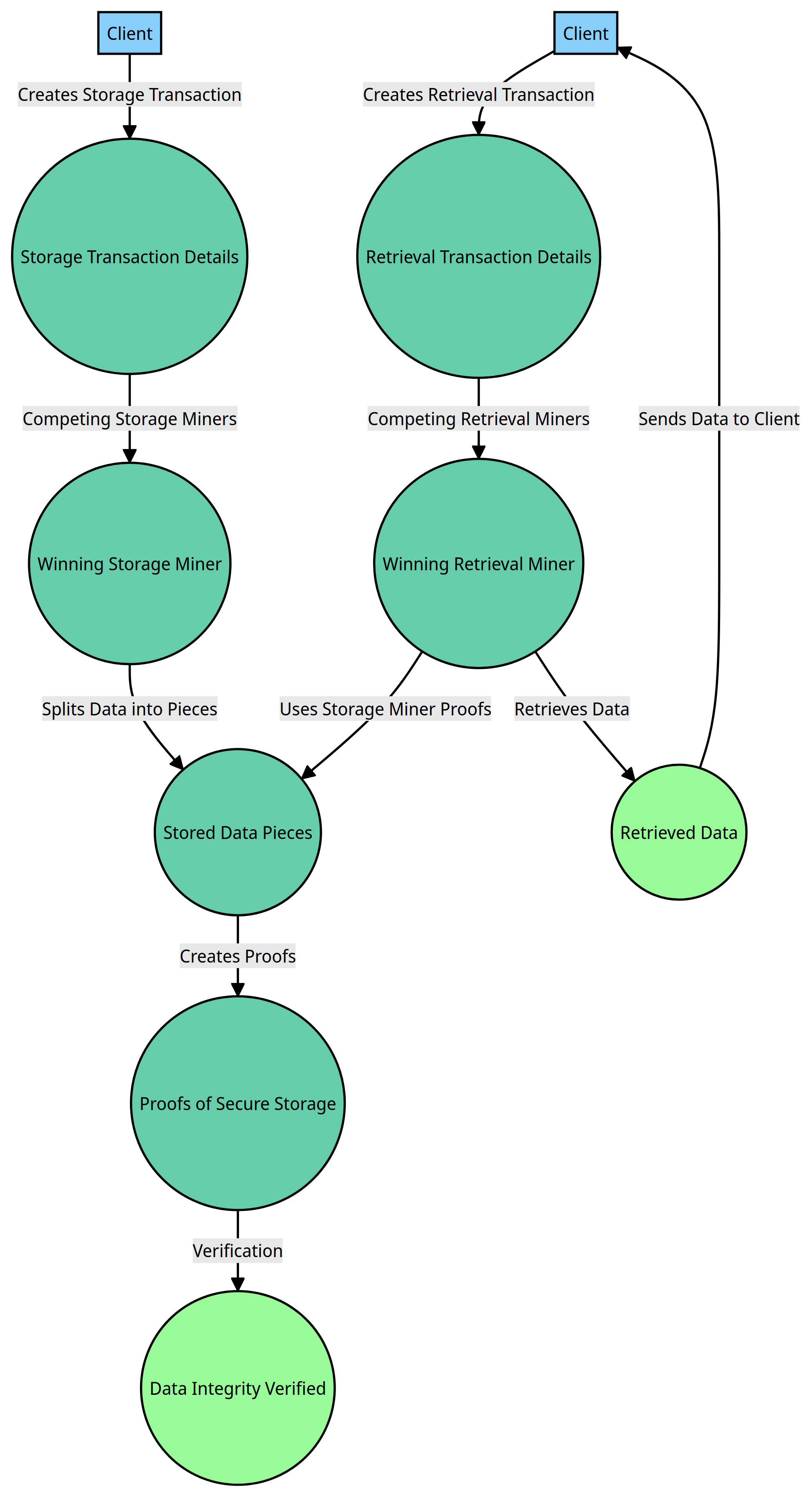
The process of storing data on Filecoin is as follows:
- A client creates a storage transaction on the blockchain, which includes information about the data to be stored, such as the size, storage time, and fee.
- Storage miners compete to win this transaction. Storage miners with more storage space and can offer lower fees are more likely to win the transaction.
- When a storage miner wins the transaction, they will split the data into smaller pieces and store it on their drives.
- Storage miners create proofs to demonstrate that they are storing the data securely. These proofs will be used to verify that the data is still intact and available when the client needs to retrieve it.
The process of retrieving data on Filecoin is as follows:
- A client creates a retrieval transaction on the blockchain, which includes information about the data to be retrieved.
- Retrieval miners compete to win this transaction. Retrieval miners that can retrieve data from other storage miners are more likely to win the transaction.
- When a retrieval miner wins the transaction, they will use the proofs of the storage miners to retrieve the data.
- The retrieval miner will send the data to the client.
FIL tokens are the native tokens of Filecoin, used to pay for storage, data retrieval, and other transactions within the network.
Filecoin has a number of advantages over centralized storage services, such as:
- Decentralization: Data stored on the Filecoin network is not controlled by any single individual or organization.
- Security: Data is split into smaller pieces and stored on multiple different computers, helping to reduce the risk of data loss.
- Affordability: Storage costs on Filecoin are typically lower than those of centralized storage services.
However, Filecoin also has some disadvantages, such as:
- Retrieval speed: Data retrieval speeds on Filecoin may be slower than those of centralized storage services.
- Scalability: The Filecoin network is still under development and may face scalability issues as the number of users increases.
Overall, Filecoin is a decentralized storage network with significant potential. Filecoin can be used to store a variety of different data types, such as personal data, enterprise data, and blockchain data.
Conclusion
This study conducted a thorough examination of centralized and decentralized data storage systems, assessing their respective merits and drawbacks.
Centralized storage, such as the Amazon AWS platform, exhibits proficiency in seamless integration with many applications and provides consistent and reliable performance. Nevertheless, the utilization of this technology can incur significant costs and presents a potential vulnerability due to its reliance on a solitary point of failure, hence posing a security concern.
The utilization of decentralized storage involves the distribution of data among multiple nodes, enhancing both the security and dependability aspects. Additionally, it facilitates the seamless transfer of data without incurring any additional expenses. Nevertheless, its current state is characterized by a deficiency in effective querying and computing capabilities. The performance of the system exhibits variability, while the development of self-service features is still ongoing.
In summary, the selection between centralized and decentralized storage is contingent upon the specific requirements and the level of sensitivity associated with the data in question. With the continuous advancement of technology, it is highly probable that both forms of storage will undergo enhancements.